Analysis — Earlier this month, Russia banned 29 British journalists, including several from the BBC and The Guardian, on the grounds that they were “associated with the defense complex”. That claim was not, at least in all cases, quite as preposterous as was widely assumed.
In part one of this two-part series, we saw how the Guardian’s Luke Harding – one of the journalists banned by Russia – has promoted entirely unsubstantiated smear stories that have hewn closely to the agenda of Western intelligence services. Harding even wrote a prominent Russiagate book and could not defend its basic claims when challenged by independent journalist Aaron Maté.
Although Russia’s ban provoked a predictable, self-righteous backlash from the U.K. media – and was adduced as further evidence of Russian president Vladimir Putin’s authoritarian tendencies – Moscow was, in fact, mirroring earlier bans by the British authorities and the European Union on Russian state-sponsored media. None of the British journalists now barred from Russia raised their voices in protest at the banning of the English-language broadcasts and the websites of RT and Sputnik.
In popular imagination, cultivated jointly by Western establishment media and Western intelligence agencies, both outlets are staffed by Russian spooks strong-arming a few impressionable Westerners with Stalinist tendencies. The reality is very different. RT wants to have influence in the West, and the only way to achieve that is by recruiting credible Western journalists who have trenchant criticisms of the Western national-security state and its war industries but cannot – for that very reason – find a platform in the establishment media at home. RT might not be the best place to get a neutral view of what Russia is up to, but it had attracted a growing audience in the West by providing an outlet for disillusioned Western journalists who are ready to paint a realistic picture of the failings of their own states.
One of RT’s journalists, for example, was Chris Hedges, a former foreign correspondent for The New York Times. He has had a long and distinguished journalistic career and has won major journalism awards. Nonetheless, six years of his Emmy-nominated “On Contact” programme for RT America – interviewing major public figures – was erased from Youtube’s channel overnight.
In part one, we considered the cases of two celebrated British journalists – Paul Mason and Carole Cadwalladr – who were revealed to be covertly colluding with Western intelligence services. Not only that, but they had used those contacts to try to harm other journalists who have been taking on the British and U.S. security states. They had been effectively recruited – or in Mason’s case, possibly recruited himself – to a covert, and dirty, information war. The paradox is that, while Cadwalladr and Mason have been accusing – without evidence – journalists in the West of colluding with foreign intelligence agencies, they themselves have been colluding with their own intelligence services to smear other reporters. If Russian intelligence needs a troll farm to spread disinformation, Western intelligence can rely, it seems, on compliant celebrity journalists in British mainstream outlets to do the same work.
Circling the wagons
Neither Cadwalladr nor Mason is likely to pay a price for their actions. In fact, they can expect to be rewarded – a sign that this kind of covert collusion is desired by establishment media, not least liberal outlets like the Guardian that try to create the misleading impression that they are somehow oppositional to the security state.
That should come as no surprise – and not just because these types of collusion work to the joint benefit of the establishment media and the intelligence services. The media outlet gets an exclusive – often one rooted in a smear operation by the state, as with Cadwalladr’s story of Farage meeting Wikileaks founder Julian Assange (documented in part one) – which they do not need to stand up beyond the simple attribution to a “well-placed”, anonymous “source”.
Meanwhile, the intelligence services set the news agenda, including with smears that target those trying to hold them to account, but cannot be scrutinized over such claims because they can shield behind anonymity. In such cases, the so-called Fourth Estate serves as simply a stenographer for the state. It amplifies the state’s self-serving allegations but adds a veneer of legitimacy through its own supposed verification via publication.
The media’s collusion, however, is not just servile. With the advent of the internet and social media, the establishment press and the intelligence services have found their interests more in tune than ever before. Independent media of the kind that seeks to hold state power to account – such as, for example, MintPress News or the Grayzone, about which Mason was so keen to spread disinformation (again, documented in part one) – or foreign channels like RT that give a platform to independent Western journalists, are treated as a threat by both the intelligence services and the establishment media.
But whereas foreign channels like RT can be easily vilified because of their ties to “enemy” states, and shut down on those grounds alone, it is more difficult to make the case for censoring independent media. It requires first a concerted campaign of Western disinformation and smears to undermine independent journalism – as we shall examine later in this article.
The powerful see such smear campaigns as vitally important. Because it is free to report stories of state crimes the establishment media mostly avoids, independent media exposes the establishment media for what it really is: the public relations arm of the state. It shows the extent to which serious, critical journalism is absent from the mainstream. And as a rival source of news, independent media leaves readers more aware of what the establishment media is choosing not to cover – and hints at why.
Paradoxically, the more effective independent media has become, the more the establishment media has circled the wagons to protect itself from this upstart media, labeling its competitors’ coverage “fake news” and “Russian disinformation”. Meanwhile, the new establishment media monopolies emerging from the digital revolution – Silicon Valley platforms like Facebook/Meta, Google/Youtube and Twitter – have gradually joined this assault, changing their algorithms to make it ever harder for people to read independent media.
Recruited to spy
If the suggestion of widespread collusion with the intelligence services by our most celebrated journalists and the establishment outlets they work for sounds improbable, consider this:
Jon Snow, who gained national treasure status in the U.K. after serving as Channel 4 News’ front man for many years, revealed in 2015 that the British intelligence services had tried to recruit him 40 years earlier, when he was an up-and-coming broadcast journalist. He was asked to spy on “left-wing” television colleagues, in return for a secret, tax-free salary that would match what he was already being paid by his employer.
Most journalists are not likely to talk of such approaches, either because they have accepted them or because disclosure might harm their careers. Snow left it until very late in his own career before mentioning the incident. But there is no reason to imagine such approaches do not continue to be made on a regular basis.
I have never written of it before – it seemed too self-aggrandising, and until now not particularly pertinent to any piece I was writing – but a decade or so ago, I was quietly “sounded out” by a British diplomat. He wanted to see if I would supply the Foreign Office with off-the-record information on my specialist subject: the Palestinian minority in Israel. I refused, and the official dropped contact.
Given that I am a left-wing, freelance journalist far from the center of power, I was left wondering how common it is for better-placed, more mainstream journalists, ones who mix regularly with British officials, to be on the receiving end of such offers. Presumably an initial, low-key approach like the one made to me is intended to see how amenable a journalist might be to becoming more involved with the intelligence services. Mutual trust is gradually built.
On the CIA payroll
Back in 1977, Carl Bernstein, who was, alongside Bob Woodward, one of the world’s most famous journalists thanks to their reporting of the Watergate scandal, turned his attention to the extent of collusion between the U.S. media and the CIA. His engagement with this contentious subject likely damaged his career – at least compared to Woodward, who spent his later years continuing to make a name for himself hanging around the Oval Office relaying insider gossip.
Bernstein’s interest in the relationship between the intelligence services and journalists probably derived from his own Watergate experiences. Ultimately, he and Woodward got their scoop – later turned into a book, then a film called “All the President’s Men” – not only through hard graft but because they were used as pawns in a high-level power battle.
As would become public knowledge in 2005, Deep Throat, the insider who gave them the leads they needed to bring down President Richard Nixon, was Mark Felt, then the FBI’s associate director and a loyalist of longtime FBI director J. Edgar Hoover. Felt had a score to settle with Nixon after he was passed over for the top job at the bureau when Hoover died.
Woodward knew Felt from his navy days, and had cultivated a relationship with his man in the FBI long before Watergate. Those long-term ties had presumably assisted them both: Felt because he could release stories that helped the bureau secretly shape the public narrative, and Woodward because he had access to information that gave him an edge over rival journalists.
Bernstein’s mammoth investigation in 1977 for Rolling Stone exposed the collusion between the CIA and journalists – collusion that had parallels with that between Woodward and Felt. Bernstein found evidence in the agency’s files that at least 400 U.S. journalists had “secretly carried out assignments for the Central Intelligence Agency”.
Bernstein observed:
“Reporters shared their notebooks with the CIA. Editors shared their staffs. Some of the journalists were Pulitzer Prize winners, distinguished reporters who considered themselves ambassadors without‑portfolio for their country. Most were less exalted: foreign correspondents who found that their association with the Agency helped their work; stringers and freelancers who were as interested in the derring‑do of the spy business as in filing articles; and, the smallest category, full‑time CIA employees masquerading as journalists abroad.”
CIA documents also showed, as Bernstein reported, that “journalists were engaged to perform tasks for the CIA with the consent of the managements of America’s leading news organizations.”
The agency particularly valued its relationship with more liberal U.S. outlets like The New York Times, Time magazine and CBS News, who were seen as more credible as vehicles for its information war. The CIA-recruited journalists signed secrecy agreements, pledging never to divulge their relationship to the agency. But in fact, as Bernstein makes clear, the existence of these CIA-journalists was an open secret in most newsrooms.
Bernstein suggests it was easy for the CIA to recruit journalists to carry out its covert work, and get editors to cooperate or turn a blind eye, because of the paranoid political climate produced by the Cold War. Journalists did not feel they were taking a side; they were supposedly involved in an existential fight to defend the right of people to live in freedom.
One has to wonder how much has changed in a world where the aggressively promoted threats of Islamist extremism, Russian “imperialism” and a more nebulous “clash of civilizations” obsess the West’s political class. Journalists are as susceptible to those fears as their predecessors were to the Cold War, and doubtless as easily manipulated.
In the shadows
Investigative journalist Nick Davies dedicated a chapter of his 2009 book “Flat Earth News” to assess how deeply the Western intelligence services had penetrated the media, at home and abroad. Ultimately, Davies concedes, it is almost impossible to know, given that such collusion necessarily happens in the shadows.
Back in the mid-1970s, around the same time as Bernstein’s work, two Congressional committees – led by Senator Frank Church and House Representative Otis Pike – had set out to investigate the matter. This was the period, we should note, when Snow was being incentivised to spy on colleagues in the U.K.
As Bernstein points out, the Church Committee mostly covered up what it found; refused to question any of the journalists involved; accepted highly redacted, or “sanitized”, documents; and was heavily swayed by senior figures from the CIA, such as William Colby and George H. W. Bush. The Pike Committee fared little better, and publication of its findings were suppressed in the U.S.
Both Congressional investigations had been triggered by concerns, post-Watergate, about the dangers of presidential abuse of the CIA’s powers and the need for greater Congressional oversight.
Under this pressure, the CIA promised to wind down its activities and banned direct payments to journalists. But the powerlessness of Congress to truly get to grips with what the CIA was up to suggests that the agency likely refashioned the program in new ways.
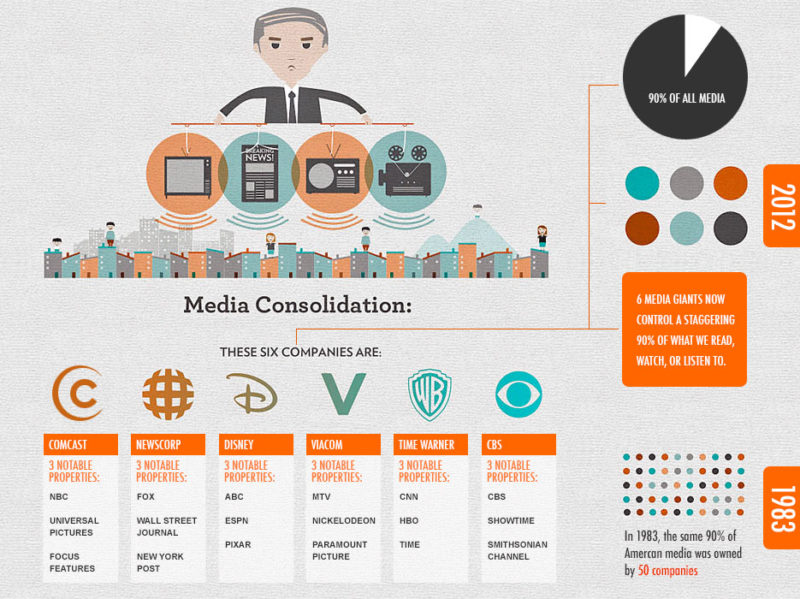
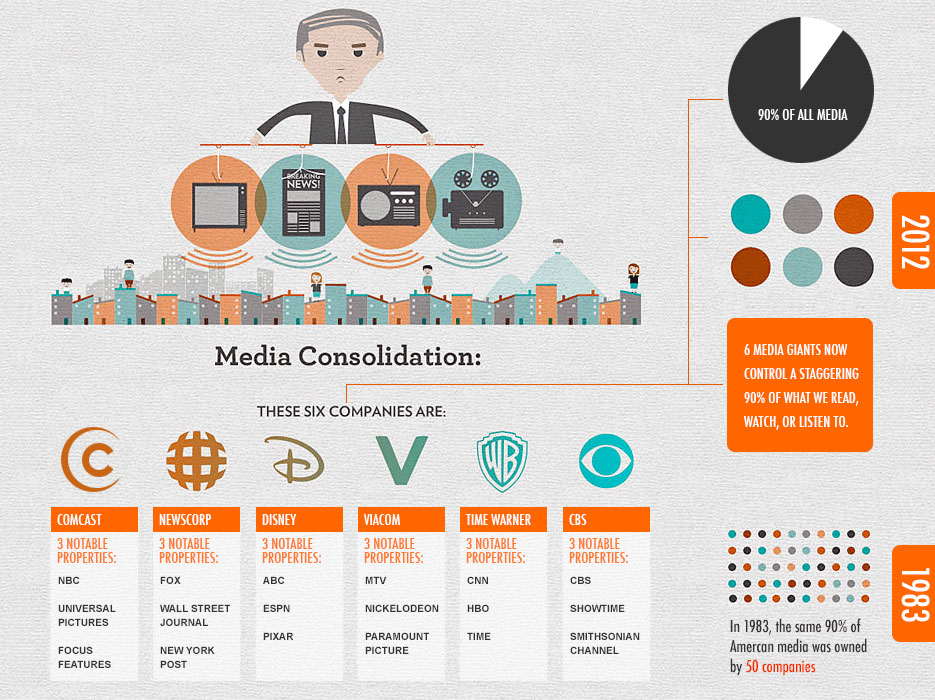
In any case, the agency’s ability to control media coverage probably grew easier over time with the concentration of media ownership. The handful of giant corporations that now control almost all mainstream media in the U.S. share most of the security establishment’s concerns, just as ordinary journalists did during the Cold War.
A paper in every capital
Nonetheless, in his book, Davies pieced together what he could from the available documents. They showed that in the post-war period the CIA had employed at least 800 covert journalist “assets” – reporters, editors, media owners – around the world, pumping out its disinformation. The figures included only those on the agency’s payroll, not those who cooperated with it, shared its aims, or were influenced by its briefings.
These journalists were likely operating as part of a wider CIA covert information war known as “Operation Mockingbird”. The aim was to conceal the agency’s covert or illegal foreign operations, such as its overthrow of democratic governments in Iran in 1953 and Guatemala in 1954, and control the media’s coverage of foreign policy fiascos such as the failed U.S.-directed invasion of Cuba’s Bay of Pigs in 1961.
To achieve these deceptions, as one CIA official admitted to the New York Times, the agency had investments in a large number of newspapers and TV stations around the world, and even covertly set up its own media outlets. “We had at least one newspaper in every foreign capital at any given time,” he said.
Operating outlets abroad meant the CIA could manipulate more convincingly the domestic news agenda. Once it had placed a false or skewed local story in an outlet it secretly owned – such as The Tokyo Evening News or Chile’s South Pacific Mail – news agencies like Reuters and Associated Press, as well as major U.S. TV stations and newspapers, could be relied on to pick it up and spread the CIA’s disinformation around the world. The agency could quickly turn the world’s media into its own echo chamber on any major topic. Thus, just as mockingbirds mimic the songs of other birds, so the media came to repeat CIA talking points.
In 1983 John Stockwell, a former head of the CIA’s Angola task force, explained on camera the ease with which the CIA channeled its propaganda through witting and unwitting journalists. “I had propagandists all over the world,” he observed. Referring to his involvement in a disinformation campaign against Cuba, he said:
“We pumped dozens of stories about Cuban atrocities, Cuban rapists [to the media]… We ran [faked] photographs that made almost every newspaper in the country… We didn’t know of one single atrocity committed by the Cubans. It was pure, raw, false propaganda to create an illusion of communists eating babies for breakfast.”
According to Stockwell, the CIA secretly sponsored the publication of thousands of propaganda books promoting its preferred angles on Vietnam, communism and U.S. foreign policy. Some of the authors, noted Stockwell, “are now distinguished scholars and journalists”.
The Pike Committee estimated conservatively from the limited documents it gained access to that almost a third of the CIA’s budget was spent on propaganda operations. It noted that the figure might be much higher. Even so, the sum was more than the combined budgets of the world’s three largest news agencies: Associated Press, UPI and Reuters.
The CIA and its British counterpart, MI6, could boast numerous agents in the foreign bureaux of all three international news agencies. The CIA even created its own news agency, sending stories to 140 newspapers around the globe.
CIA agents were also found to have been working in the most prestigious U.S. media outlets. The New York Times employed at least 10 of them. At various times, Newsweek’s editor, foreign editor, Washington bureau chief and a host of reporters were on the CIA’s books. Time magazine, Reader’s Digest and the Christian Science Monitor all cooperated closely with the agency. American television networks routinely allowed the CIA to monitor their newsrooms.
Davies cites a report in the Guardian from 1991 that the CIA was found to have made payments to 90 British journalists. MI6 presumably had a separate, and at least as large, cadre of senior U.K. journalists on the payroll.
During that period, Britain ran its own propaganda unit, the Information Research Department (IRD), which cultivated journalists in similar ways to the CIA. Its task, according to Declassified U.K., was “to discredit human rights figures, undermine political opponents overseas, help overthrow governments, and promote U.K. influence and commercial interests around the world.” The British government also used the IRD to damage anyone perceived to be a domestic opponent.
Earlier this month, Declassified U.K. revealed that, in 1971, the Australian government set up its own unit modeled on Britain’s IRD and recruited senior Australian journalists to collaborate with it.
Credulous reporting
It would be foolish to imagine that, in this more complex information age, the U.S. and U.K. intelligence services’ influence over journalists has diminished. Both Cadwalladr and Mason’s cases illustrate how intimate those ties still are.
The New York Times “let go” one of its star reporters, Judith Miller, in 2005. Her reports of the threat posed by Saddam Hussein’s weapons of mass destruction – coverage that was critical to rationalizing the 2003 invasion of Iraq in violation of international law – were utterly discredited by later developments. There were no WMDs in Iraq. Western inspectors had consistently said this, but their voices were drowned out by pro-war media. Miller, who claimed she was given special Pentagon security clearance, had been fed stories by U.S. intelligence agencies. She had acted as an uncritical conduit for CIA disinformation that was then repeated by other major outlets.
She was far from alone in channeling fake news from intelligence agencies in the lead-up to the Iraq invasion. The New York Times apologized for its mistakes, promising it would learn from the episode. But it has been just as credulous in regurgitating the intelligence services’ claims in recent U.S. proxy wars and regime change attempts – in Libya, Syria, Yemen, Iran, Venezuela and elsewhere. Miller was not sacked because she served as a willing channel for Western disinformation. Rather, real-world events required the New York Times to make someone a sacrificial victim for its all-too-obvious failings over Iraq. She was the ideal scapegoat.
Institutional collusion with the intelligence services has also become all too evident at the Guardian, the New York Times’ U.K. counterpart. Declassified U.K. has documented how the the Guardian has been increasingly co-opted by the British intelligence services after its publication in 2013 of the Edward Snowden leaks. Among other things, those leaks revealed that the U.S. and U.K. were operating secret and illegal mass surveillance programmes.
At that time, the Guardian, unlike other British media outlets, had a well-publicized opposition to taking part in the supposedly voluntary D-notice system, run by the Ministry of Defense, to regulate information that might threaten national security. After the initial Snowden revelations from the Guardian, the D-Notice Committee issued a notice against further publication of information released by Snowden. Most British outlets either ignored the leaks or offered minimal coverage. The Guardian, however, defied the government’s advice.
Shortly afterwards, officials from GCHQ, Britain’s equivalent of the National Security Agency, arrived at the paper and ordered it to destroy the laptops containing the Snowden material. The paper complied, with deputy editor Paul Johnson overseeing the destruction. Soon, the D-Notice Committee was able to report that “engagement” with the Guardian was strengthening and there was “regular dialogue” with its staff. The “culmination”, as the committee referred to it, was Paul Johnson’s agreement to sit on the committee itself.
When in 2015 the Guardian appointed a new editor, Katharine Viner, whose background was in fashion journalism, the security services appeared to seize the chance to lure the newspaper into greater cooperation. A year later the paper boasted that it secured the “first newspaper interview given by an incumbent MI5 chief in the service’s 107-year history” – MI5 being Britain’s domestic intelligence service. The article was co-written by Johnson and headlined on Russia – what else – as a “growing threat” to the U.K. The Guardian would follow up with exclusive interviews with the heads of MI6 and with the U.K.’s most senior counter-terrorism officer. All were softball interviews in which the British security state was allowed to set the agenda.
Under Viner, a host of investigative journalists with experience of covering national security issues departed. A former Guardian journalist told Declassified U.K.,
“Effective scrutiny of the security and intelligence agencies – epitomized by the Snowden scoops but also many other stories – appears to have been abandoned… [It] sometimes seems the Guardian is worried about upsetting the spooks.”
Instead, the paper has focused on targeting those who are in the crosshairs of the intelligence services – most obviously Julian Assange, whose publication of leaked official documents in 2010 exposed U.S. and U.K. war crimes in Iraq and Afghanistan. In recent years, as the U.S. has sought Assange’s extradition so it can lock him out of sight for up to 175 years, the Guardian has run a series of barely credible stories that appear to have been supplied to it by the intelligence services and clearly serve its interests. Those hit-pieces include articles written by Carole Cadwalladr and Luke Harding, and were discussed in part one.
As Declassified U.K. noted, the Guardian was also key to injecting credibility into a relentless media campaign to smear the then left-wing leader of Britain’s Labour party, Jeremy Corbyn. He was variously portrayed as a national security threat, a traitor and an antisemite. Again, the fingerprints of the security services were all over these stories. They had begun with an anonymous army general, interviewed by The Sunday Times, warning that the military “would use whatever means possible, fair or foul, to prevent” Corbyn becoming prime minister. The Guardian’s uncritical echoing of evidence-free claims of an antisemitism problem in Labour under Corbyn was particularly damaging because so many of the paper’s readers were traditional Labour voters.
Disappearing neo-Nazis
The intelligence services’ cultivation of ties with journalists in an increasingly digital, more defused media environment is likely to be as covert as ever. But there are occasional, brief glimpses of what they may be up to. As mentioned in part one, it emerged in 2018 that national clusters of journalists, along with academics and politicians, were working with the opaque Integrity Initiative, a covert operation supposedly against “Russian disinformation” supported by the British Foreign Office and Defense Ministry. The Initiative’s registered address in Scotland turned out to be an abandoned, semi-derelict mill. Its real offices were eventually tracked down to a plush part of central London.
The Integrity Initiative’s British cluster included some well-known names in British journalism. Its real aim was – once again – to paint independent media and left-wing politicians critical of Western wars as in the pocket of Russia and Vladimir Putin. The Initiative was also found to have been involved in efforts to bring down Corbyn.
The media’s memory-holing of the Snowden revelations and its silence on Assange’s persecution – despite the very obvious threat posed to a free press – are themselves an indication of the degree to which the establishment media share the aims of the security state and are complicit in its narrative manipulations.
Coverage of the West’s recent proxy wars have provided further clues as to the extent of that collusion. It has been hard to ignore the establishment media’s uncritical promotion of narratives in Syria and Ukraine that look suspiciously like they were crafted by Western intelligence agencies. That has involved some stunning about-turns in their coverage that should set alarm bells ringing with observers.
In Ukraine, that has been evident in the media’s frantic efforts to obscure its own recent concerns about neo-Nazi groups like the Azov Battalion being integrated into the Ukrainian military, and portray any attempt to remind us of that earlier coverage as Russian disinformation.
Those maneuvers echo similarly desperate moves by the establishment media to obscure the fact that groups allied to al-Qaeda and Islamic State ended up comprising the bulk of the “rebel” forces in Syria. Only a short time earlier, both had been regarded as the West’s most fearsome foes.
Russia was revived as the West’s number one enemy about the time the media – and the intelligence services – found themselves unable to continue fearmongering about Islamist extremists because those groups needed to be transformed into our allies in Syria.
In both conflicts, it has been hard not to notice too how easily the establishment media has been swayed not by facts on the ground but by what look more like branding exercises guided by Western marketing firms.
Ukraine’s president, Volodomyr Zelensky, reportedly took time out of his schedule last week to brainstorm with “marketing professionals” at Cannes about how to use “creative ingenuity” to keep the war in the spotlight, after earlier opening the film festival. Last week too, he made an appearance on a giant video screen at the popular Glastonbury music festival in the U.K. On each occasion, wore his now-signature designer wartime outfits.
White Helmets ringfenced
Similarly, the White Helmets have received unquestioning adulation from the Western media. A hagiographic documentary on their work was even awarded an Oscar. Yet the mysterious emergency rescue outfit appears only to work in areas of Syria controlled by jihadist groups the West has previously opposed for their human rights abuses and mistreatment of women and girls.
Liberal media has gone all-out to ringfence the White Helmets – and their jihadist allies – from journalistic and academic scrutiny. Independent journalists brave, or foolish, enough to try to break through this cordon sanitaire have found themselves smeared, and accused of spreading disinformation on Russia’s behalf. Western intelligence agencies have every incentive to malign these critics because the White Helmets are a central pillar upholding claims that Syrian president Bashar al-Assad, assisted by Russia, used chemical weapons against his own people in rebel-held areas.
If the White Helmets are a credible, neutral humanitarian movement – a Syrian version of the Red Cross – then the media might be justified in treating their claims of atrocities by Assad uncritically. But if they are really a partisan rescue service involved in rebranding Islamist extremism to promote the goal of Western-sponsored regime change in Syria, then the media needs to be skeptical and scrutinize their every assertion. The establishment media has adopted the first approach, ignoring any indication that the White Helmets might not be quite what they seem.
That failure has been thrown into especially stark relief by the media’s extraordinary refusal to publicize the testimonies of whistleblowing inspectors at the Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW). Those whistleblowers say their findings at one site of an alleged chemical attack, at Douma in 2018, were rewritten by their own management under threats from the U.S.
The media’s silence is all the more astounding given that Jose Bustani, a former head of the OPCW, and Hans von Sponeck, the U.N.’s former chief weapons inspector in Iraq, have found the whistleblowers’ allegations credible and urged that they be investigated.
The story, if confirmed, has the potential to unravel much of the narrative in Syria jointly promoted by the Western intelligence services and the establishment media. Which is why any effort to examine it more closely is being crushed. If Douma was a staged attack rather than one carried out by Assad’s forces, as the whistleblowing inspectors’ evidence suggests, it would implicate the White Helmets in the deception – and possibly the murder of the civilians alleged to have been gassed in Douma. It could also mean that other chemical attacks assigned to Assad might have been the responsibility of jihadists.
That is why the stakes are so high. It may also explain why there has been an incessant stream of stories in liberal media outlets shoring up the Western narrative by smearing once again as a Russian asset any journalist tackling the subject in a critical manner.
The media’s defamation campaigns have been assisted by various, “expert” bodies, seemingly cut-outs covertly funded by Western governments, such as Bellingcat, the Institute for Strategic Studies (the parent “charity” of the Integrity Initiative) and, most recently, the Institute for Strategic Dialogue. These organizations produce smear-laden reports on which the establishment media builds its hollow case against independent media.
This month, the Guardian ran the latest of its evidence-free smear pieces designed to silence independent journalists and protect the White Helmets. The article accuses independent journalists of being part of a supposedly Russian-backed disinformation “network”. The piece implicitly discredits the OPCW whistleblowers by ignoring their existence and instead attributing their claims to “a core of 28 conspiracy theorists”.
Despite its grand claims, the paper provides no evidence of any collusion between Russia and the named independent journalists, or even between the journalists themselves, that might justify labeling them a network, let alone a Russian-backed one. Nor does the article provide any examples of what disinformation these journalists are supposedly spreading – apart from their questioning of the actions of Western states.
In The Guardian, @TownsendMark calls me “the most prolific spreader of disinformation” on Syria. His source is a study by the ISD think tank.
Mark has failed to:
-contact me
-offer an example of my alleged “disinformation”
-disclose that ISD is funded by US, UK & allied states pic.twitter.com/qnmN7npYr9— Aaron Maté (@aaronjmate) June 19, 2022
Aaron Maté, who is named, has been one of the main channels by which the OPCW whistleblowers have been able to make public their concerns about the organization’s tampering with their findings in its final report. And yet the Guardian makes no mention that Maté’s supposed “disinformation” is actually sourced directly from OPCW inspectors themselves. The Guardian article is, in fact, exactly what it accuses independent media of being: pure disinformation (from Western intelligence agencies).
The BBC has been ready with the smears too. It ran an extraordinarily lengthy, though flimsy, podcast series trying to shore up the humanitarian credentials of James Le Mesurier, a former U.K. military intelligence officer who founded the White Helmets in 2014. Shortly after he had been accused of embezzling donor money, Le Mesurier fell to his death from an apartment in an Istanbul building, in what was judged to be a suicide.
The BBC series, “Mayday”, however, spent an inordinate amount of time trying to deflect attention from these facts. Instead, it sanitized Le Mesurier and the White Helmets’ reputation, implied independent journalists and academics had tipped Le Mesurier into suicide through their criticisms, and, like the Guardian, sought to discredit the OPCW whistleblowers.
MI6 could not have done a better job. When Maté posed a series of questions over the programme’s “smears, gaping omissions, leaps of logic, and factual errors”, Mayday’s producers went to the ground. The BBC journalist who fronted Mayday, Chloe Hadjimatheou, repeated the formula last month for BBC Radio 4 with “Ukraine: The Disinformation War”, covering much the same ground and defaming many of the same targets. Once again, Hadjimatheou has failed to respond to criticisms.
Real-world Marvel Universe
There are a whole raft of reasons why journalists working for the establishment media end up parroting the narratives of Western intelligence agencies engaged in an information war against critics that very much include independent media.
It would be naïve in the extreme to imagine that the establishment media severed its well-documented connections with the intelligence services back in the 1970s. Some journalists are doubtless still on the payroll and operating covertly, even if that number is probably small. Most, however, don’t need payment. By temperament and circumstance, they are extremely susceptible to the West’s sophisticated influence campaigns.
The tools at the disposal of Western security services, so ready to accuse Russia of using troll farms, grow all the time. The West has its own troll armies, enthusiastically spreading the work of intelligence cut-outs like Bellingcat and the Institute for Strategic Studies.
Last year, Newsweek revealed an undercover army of at least 60,000 operatives run by the Pentagon that used “masked identities” to exert influence on the digital world: “The explosion of Pentagon cyber warfare, moreover, has led to thousands of spies who carry out their day-to-day work in various made-up personas, the very type of nefarious operations the United States decries when Russian and Chinese spies do the same.”
There are a variety of reasons why journalists working for establishment media outlets so readily follow scripts written for them by Western intelligence agencies. In part, journalists successful in establishment media are products of lengthy selection processes effected through their upbringing, social class and education. Those who reach influential media positions are sympathetic to, and easily swayed by, the kinds of narratives that present Western states as the good guys fighting evil foes and Western crimes as unfortunate mistakes that cannot be compared to the atrocities committed by enemies. Like the public, Western journalists are socialized to interpret events as though we inhabit a real-world Marvel universe where our side is a mix of Captain America and Iron Man. As Noam Chomsky once observed to the BBC’s Andrew Marr during an interview:
“I’m not saying you’re self-censoring. I’m sure you believe everything you’re saying. But what I’m saying is that, if you believed something different, you wouldn’t be sitting where you’re sitting.”
In any case, Western journalists work inside large media corporations where they will not survive long unless they submit – mostly unconsciously – to the dominant corporate culture. Further proving Chomsky’s point, Marr claimed on another occasion that his “Organs of Opinion were formally removed” when he began working at the BBC. It was an extreme, fundamentalist view that suggested Marr believed he and the BBC – funded by, and accountable to, the British state – were able to divine absolute, eternal truths that they then disinterestedly passed on to viewers.
In fact, as the consolidation of corporate America continues, the situation for critically-minded journalists working in the establishment media grows ever worse. Media corporations have diversified their interests in ways that entrench them even more deeply in a neocolonial ideology that seeks both absolute control over global resources and their exploitation, and profits from the war, surveillance and security industries that enforce that control.
It is no accident that media corporations produce Hollywood fare that encourages the Western public to identify with superheroes and reduces the world to black-and-white struggles. Independent journalists trying to question this simple-minded narrative are easily cast as Thanos.
Read More:
How the Pentagon Leaned on Hollywood to Sell the War in Afghanistan
On top of that, any journalist trying to look into the darkest corners of Western foreign policy can be herded back into the fold through threats – if not from their editors, then from the security services, as the Guardian’s Paul Johnson experienced at first hand. The security state has plenty of tricks up its sleeve. Complicit social media can punish independent-minded reporters through its algorithms, starving them of readers. Complicit online financial services like PayPal can punish independent journalists by starving them of income, as happened to MintPress and Consortium News. And if all that fails, there is always the example of Julian Assange, whose head has been displayed on a pike in London over the past decade – as was once the norm in Medieval times for those who angered the king – initially outside the Ecuadorian embassy and now outside Belmarsh high-security prison.
In the circumstances, it is surprising that there are any journalists left who are not simply regurgitating what the intelligence services tell them. The rapid rise of independent media may soon look like a brief, digital aberration in our media landscape – unless we dig in and fight the security state to keep the spirit of critical journalism alive.
Jonathan Cook is a MintPress contributor. Cook won the Martha Gellhorn Special Prize for Journalism. His latest books are Israel and the Clash of Civilisations: Iraq, Iran and the Plan to Remake the Middle East (Pluto Press) and Disappearing Palestine: Israel’s Experiments in Human Despair (Zed Books). His website is www.jonathan-cook.net.
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect MintPress News editorial policy.
The post How Spooks and Establishment Journalists Are Circling The Wagons appeared first on MintPress News.